PBR基础
读Abedo的Guidebook时,发现有一些以前没注意的细节,也在这里补一下笔记。
- Metal-Roughness工作流
- Pros
- 非金属统一使用0.04的F0,不容易出错
- 纹理内存使用量小(metal、roughness都只需要单通道)
- Cons
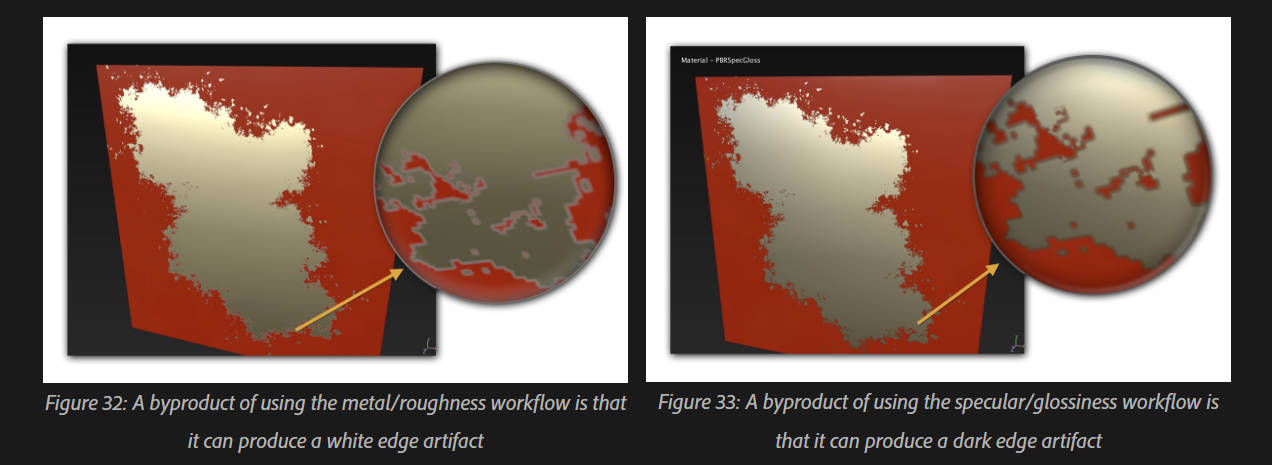
- 低分辨率下edge artifact更明显
- Specular-Glossiness工作流
- Specular可调配非金属F0,一般为2%~5%,即40 ~ 75 sRGB
- Glossiness可视为1-roughness
- Pros
- 可以设置非金属F0
- 低分辨率下edge artifact不明显
- Cons
- 容易出错使能量不守恒
- 纹理内存使用量大
Reference: PBR-理论 LearnOpenGL CN PBR-直接光照 LearnOpenGL CN PBR-IBL LearnOpenGL CN The PBR Guide - Part 1 AbedoSubstance The PBR Guide - Part 2 AbedoSubatance
直接光照Shader
其中的DFG函数可表示如下:
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
float DistributionGGX(vec3 N, vec3 H, float roughness)
{
float a = roughness*roughness;
float a2 = a*a;
float NdotH = max(dot(N, H), 0.0);
float NdotH2 = NdotH*NdotH;
float nom = a2;
float denom = (NdotH2 * (a2 - 1.0) + 1.0);
denom = PI * denom * denom;
return nom / denom;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
float GeometrySchlickGGX(float NdotV, float roughness)
{
float r = (roughness + 1.0);
float k = (r*r) / 8.0;
float nom = NdotV;
float denom = NdotV * (1.0 - k) + k;
return nom / denom;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
float GeometrySmith(vec3 N, vec3 V, vec3 L, float roughness)
{
float NdotV = max(dot(N, V), 0.0);
float NdotL = max(dot(N, L), 0.0);
float ggx2 = GeometrySchlickGGX(NdotV, roughness);
float ggx1 = GeometrySchlickGGX(NdotL, roughness);
return ggx1 * ggx2;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
vec3 fresnelSchlick(float cosTheta, vec3 F0)
{
return F0 + (1.0 - F0) * pow(clamp(1.0 - cosTheta, 0.0, 1.0), 5.0);
}完整的片段着色器构成如下。案例场景中有四个点光源,对每一个点光源进行遍历后叠加环境光即可。
vec3 N = getNormalFromMap();
vec3 V = normalize(camPos - WorldPos);
// calculate reflectance at normal incidence; if dia-electric (like plastic) use F0
// of 0.04 and if it's a metal, use the albedo color as F0 (metallic workflow)
vec3 F0 = vec3(0.04);
F0 = mix(F0, albedo, metallic);
// reflectance equation
vec3 Lo = vec3(0.0);
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
// calculate per-light radiance
vec3 L = normalize(lightPositions[i] - WorldPos);
vec3 H = normalize(V + L);
float distance = length(lightPositions[i] - WorldPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (distance * distance);
vec3 radiance = lightColors[i] * attenuation;
// Cook-Torrance BRDF
float NDF = DistributionGGX(N, H, roughness);
float G = GeometrySmith(N, V, L, roughness);
vec3 F = fresnelSchlick(max(dot(H, V), 0.0), F0);
vec3 numerator = NDF * G * F;
float denominator = 4.0 * max(dot(N, V), 0.0) * max(dot(N, L), 0.0) + 0.0001; // + 0.0001 to prevent divide by zero
vec3 specular = numerator / denominator;
// kS is equal to Fresnel
vec3 kS = F;
// for energy conservation, the diffuse and specular light can't
// be above 1.0 (unless the surface emits light); to preserve this
// relationship the diffuse component (kD) should equal 1.0 - kS.
vec3 kD = vec3(1.0) - kS;
// multiply kD by the inverse metalness such that only non-metals
// have diffuse lighting, or a linear blend if partly metal (pure metals
// have no diffuse light).
kD *= 1.0 - metallic;
// scale light by NdotL
float NdotL = max(dot(N, L), 0.0);
// add to outgoing radiance Lo
Lo += (kD * albedo / PI + specular) * radiance * NdotL; // note that we already multiplied the BRDF by the Fresnel (kS) so we won't multiply by kS again
}
// ambient lighting (note that the next IBL tutorial will replace
// this ambient lighting with environment lighting).
vec3 ambient = vec3(0.03) * albedo * ao;
vec3 color = ambient + Lo;
// HDR tonemapping
color = color / (color + vec3(1.0));
// gamma correct
color = pow(color, vec3(1.0/2.2));
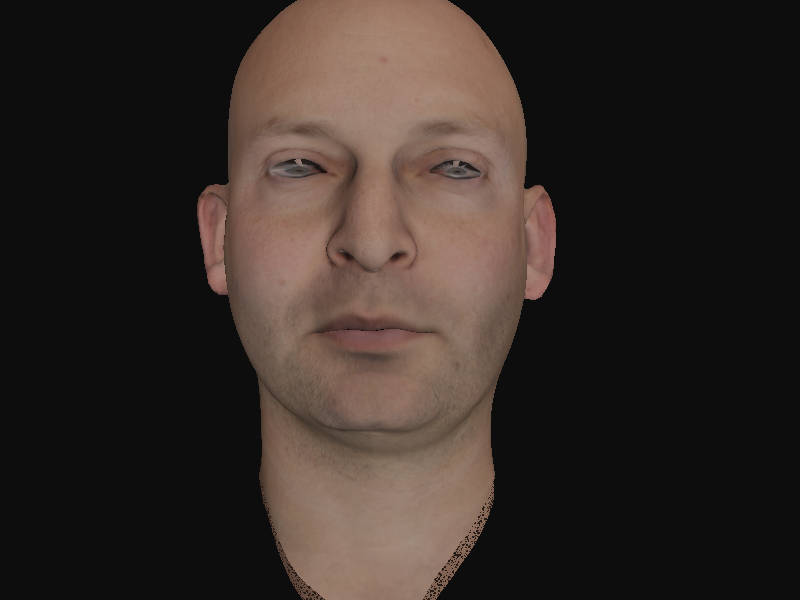
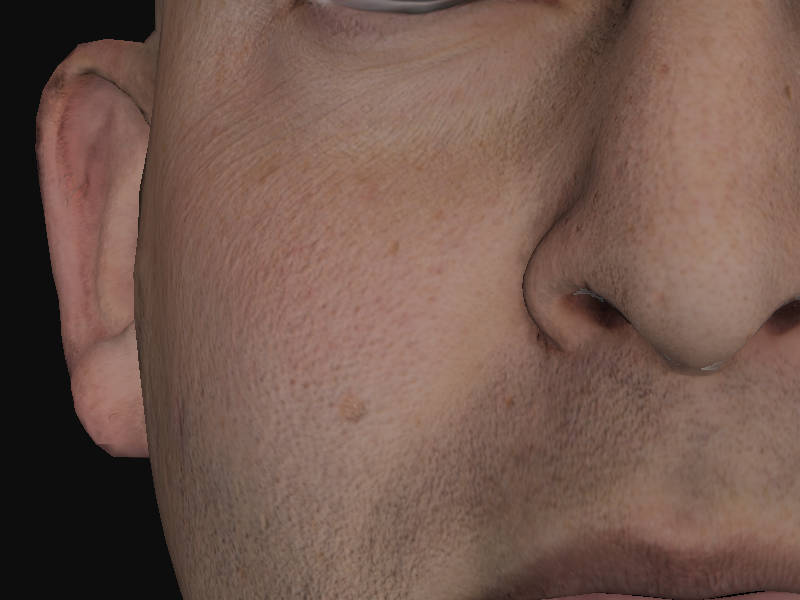
作业素材提供了一张灰度值的"specular"贴图,我们就当作glossiness来用了,渲染获得的头部模型如下:
 看看毫无投射的面部毛孔——
看看毫无投射的面部毛孔——
 下一节我们从前向渲染换延迟渲染,然后准备算曲率!
下一节我们从前向渲染换延迟渲染,然后准备算曲率!